In this Article we are gonna see how CSMA/CD(Carrier Sense Multiple Accesse/Collision Detection) works and why we needed it. I wrote “needed” because we don’t use Hub anymore, which based on CSMA/CD method. Nowaday we use switchs. A switch doesn’t need CSMA/CD method, cause it has its own process, which a Hub doesn’t have. But to learning the Knowledge, we are gonna see it with Animation.
CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collesion Detection)

The first Ethernet corresponds to a bus topology, which multiple stations are connected (Multiple Access). It is stipulated that all stations can read the signals on the bus but can not transmit them at the same time. Which of the connected stations is allowed to send is determined by the CSMA / CD method, which works according to the “Listen Before Talk” principle.
All stations permanently listen to the transmission medium (Carrier Sense). They can distinguish between a free and an occupied transmission medium. With a free transmission medium can be sent. If one Station want something, it will check if the bus is free. If it is free, the station begins to send. This means that it puts the data signal on the bus.
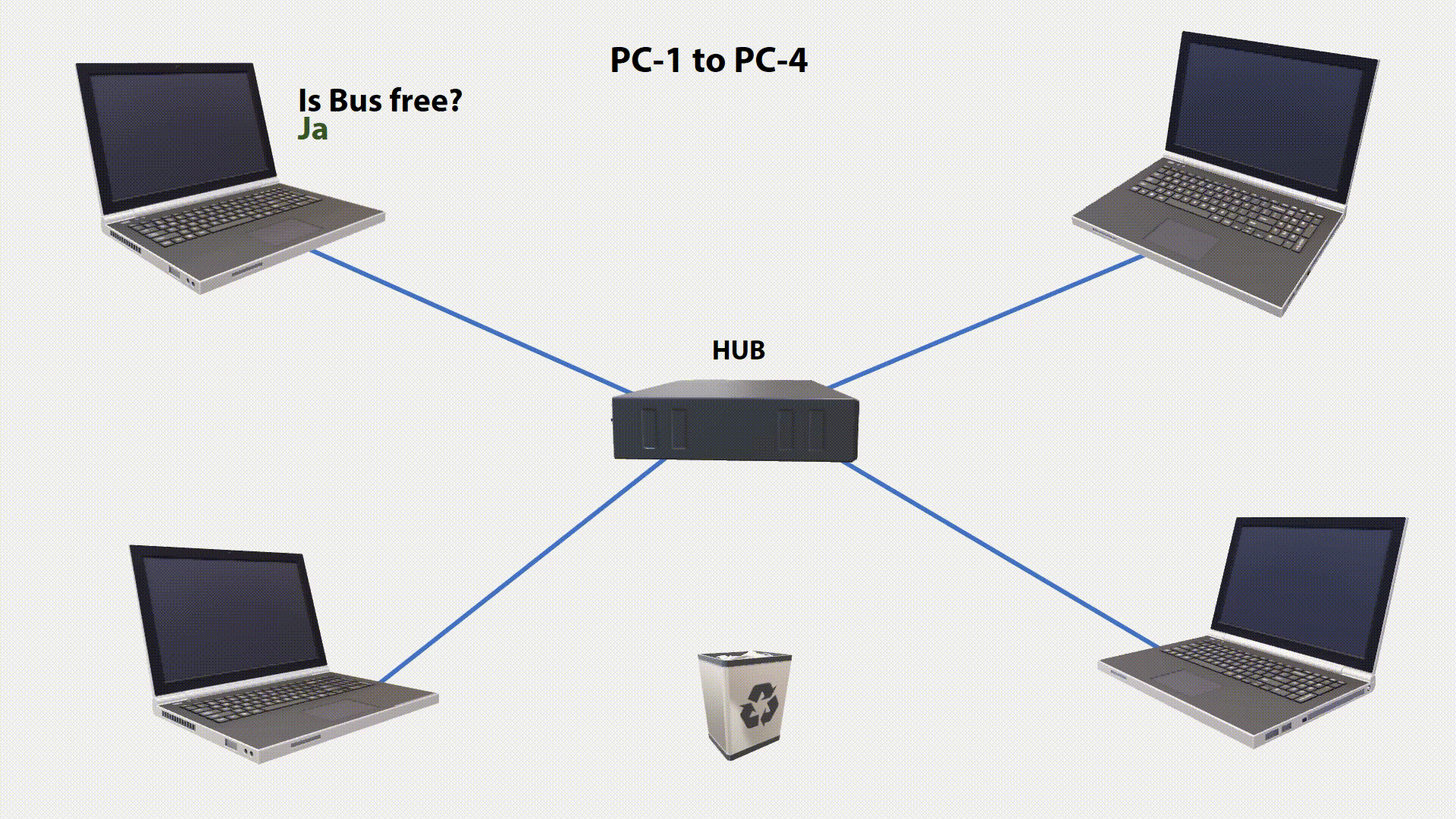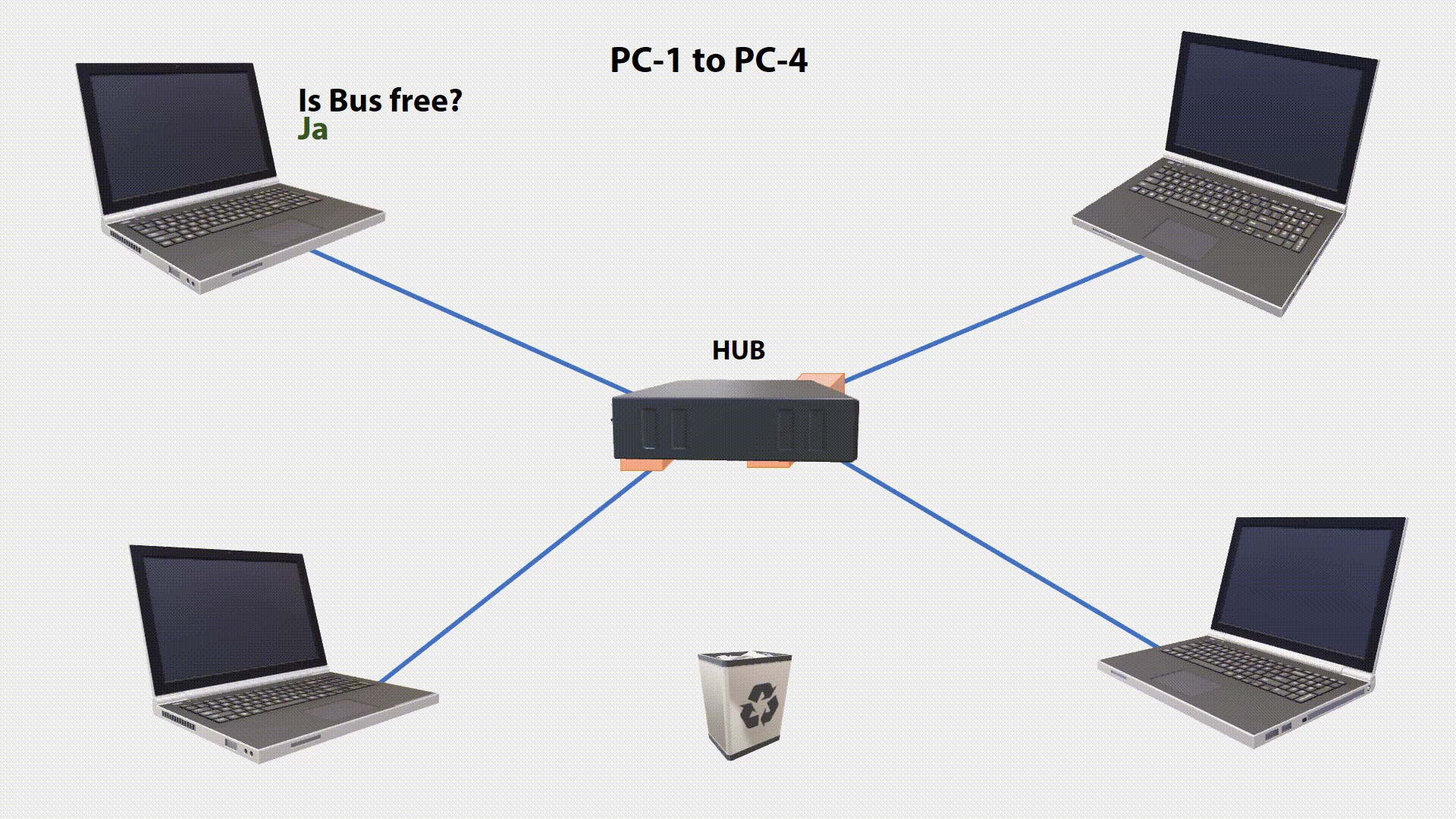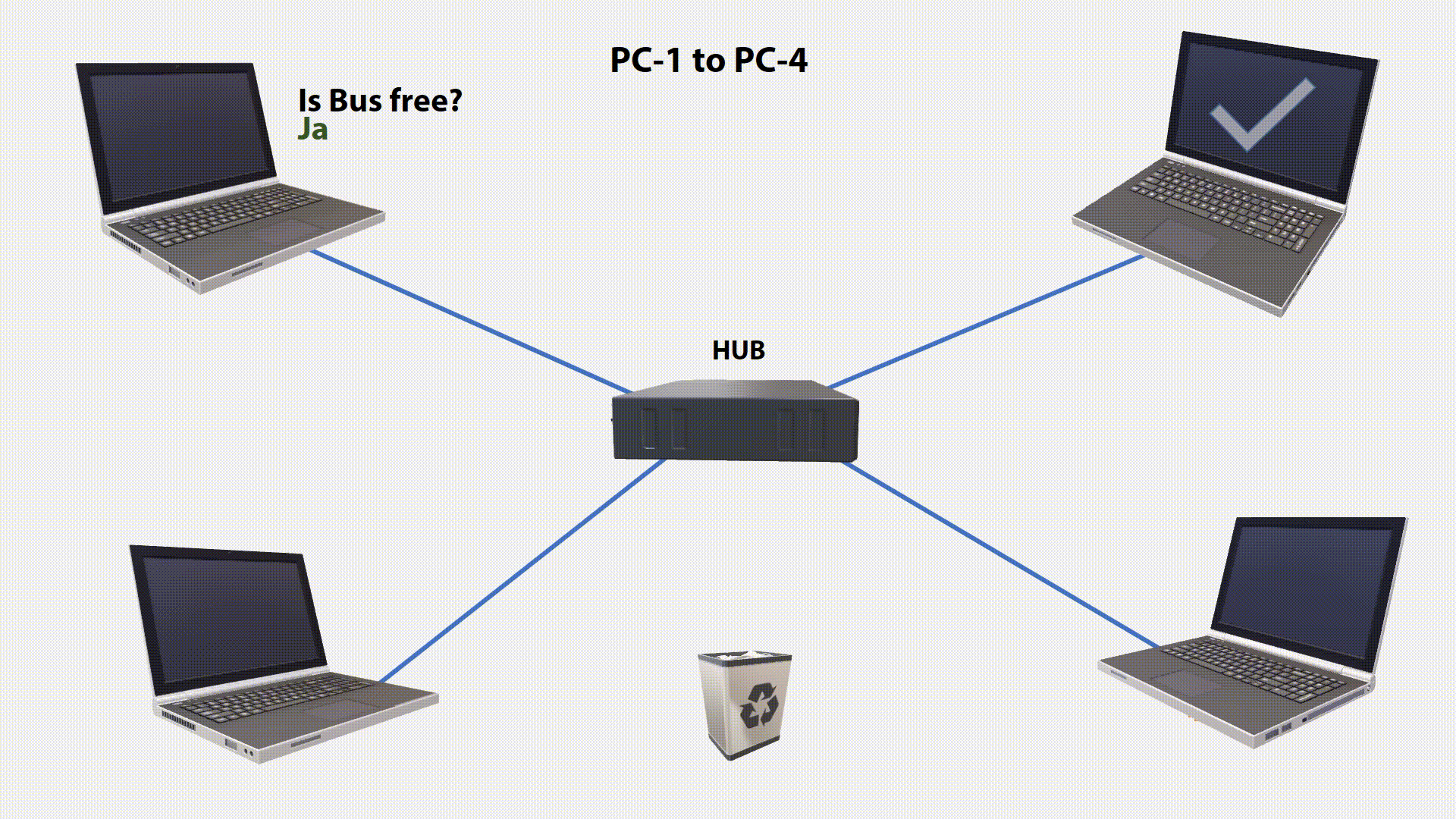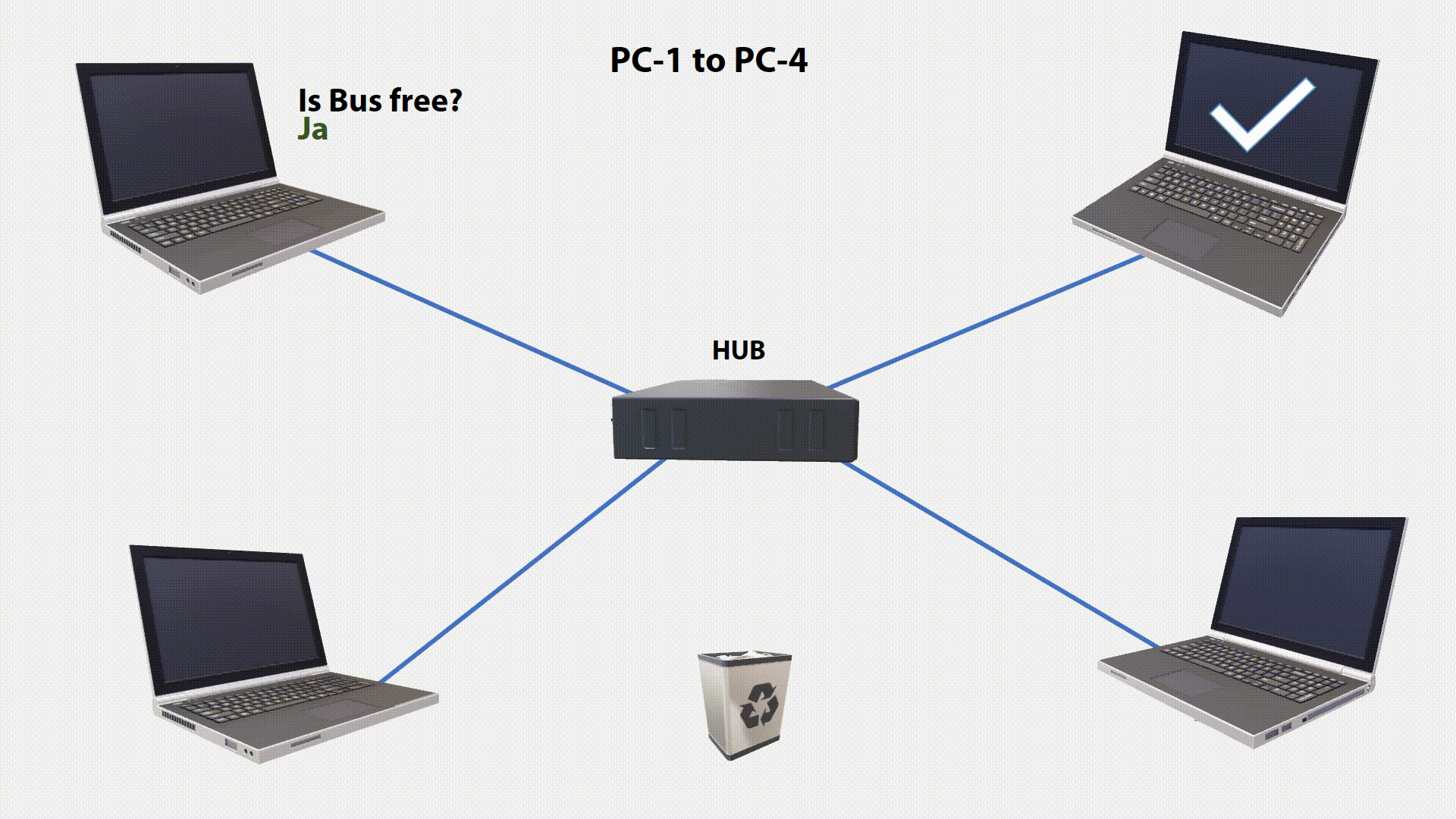
During signal transmission, the station checks if the transmitted signal is identical to the signal on the bus. If the signal sent does not correspond to the monitored signal, another station has sent at the same time. The two signals will superimposed. This condition on the transmission medium is called a Collision. By permanently checking the condition on the line, this collision can be detected (Collision Detection).
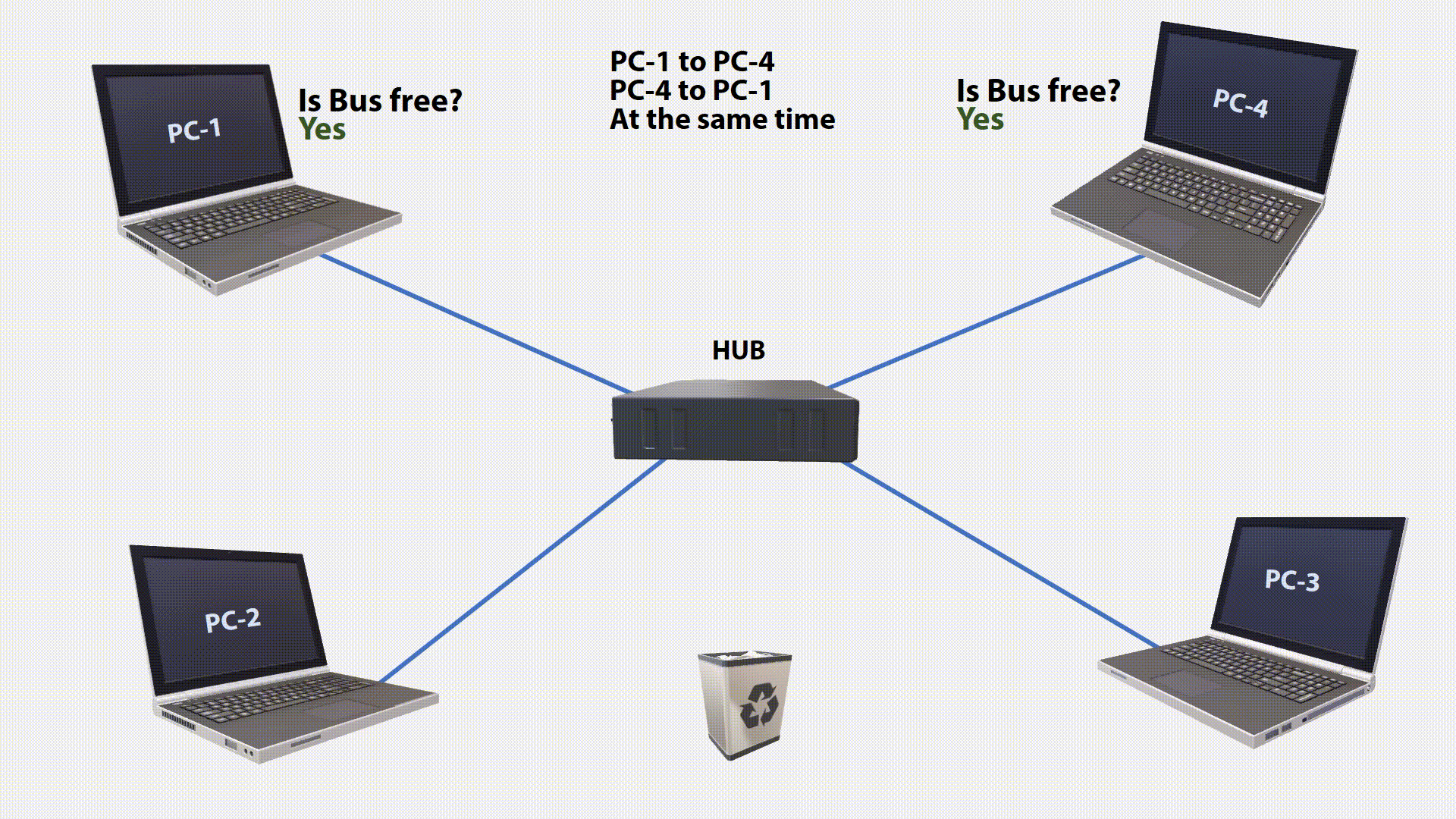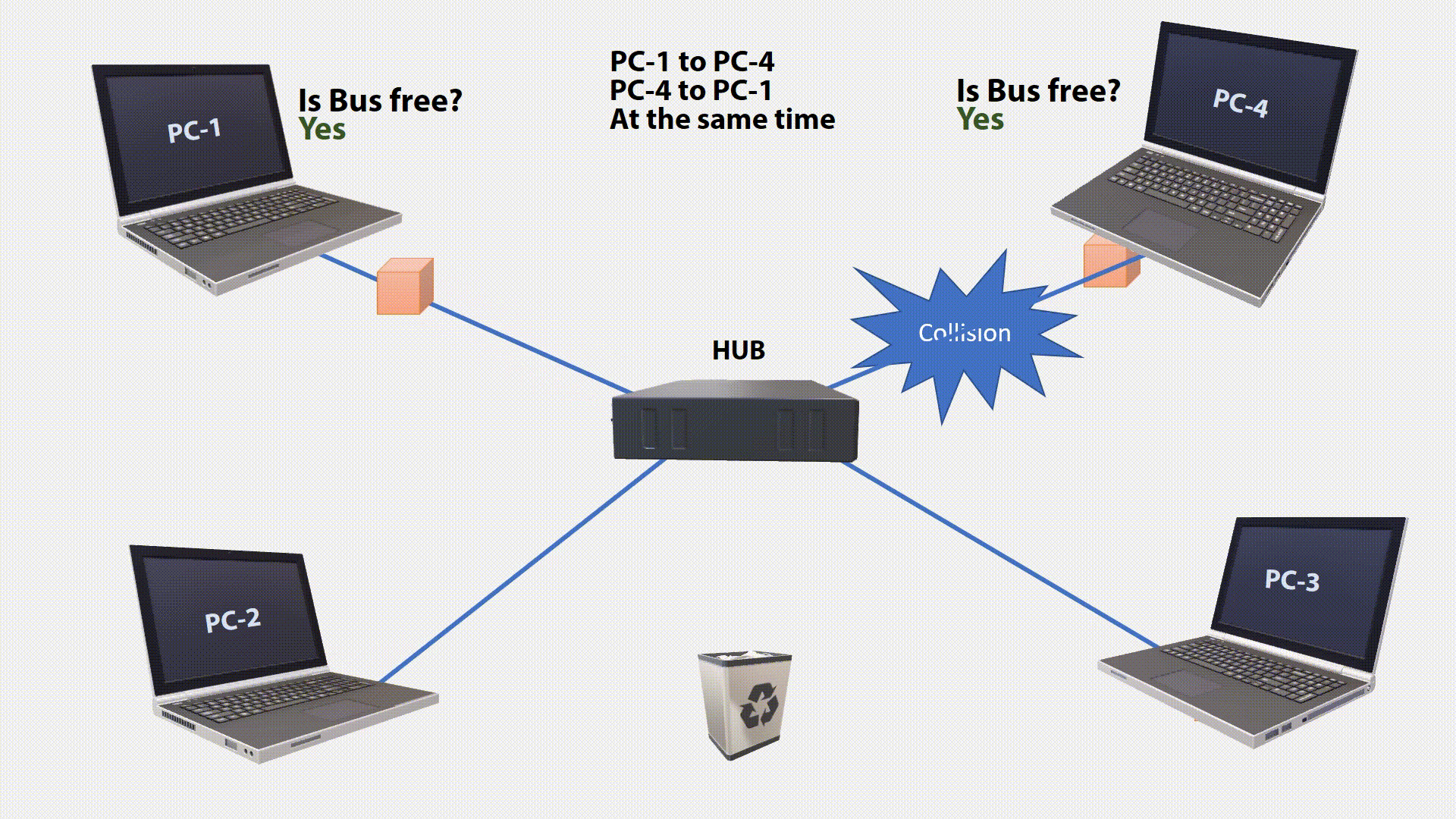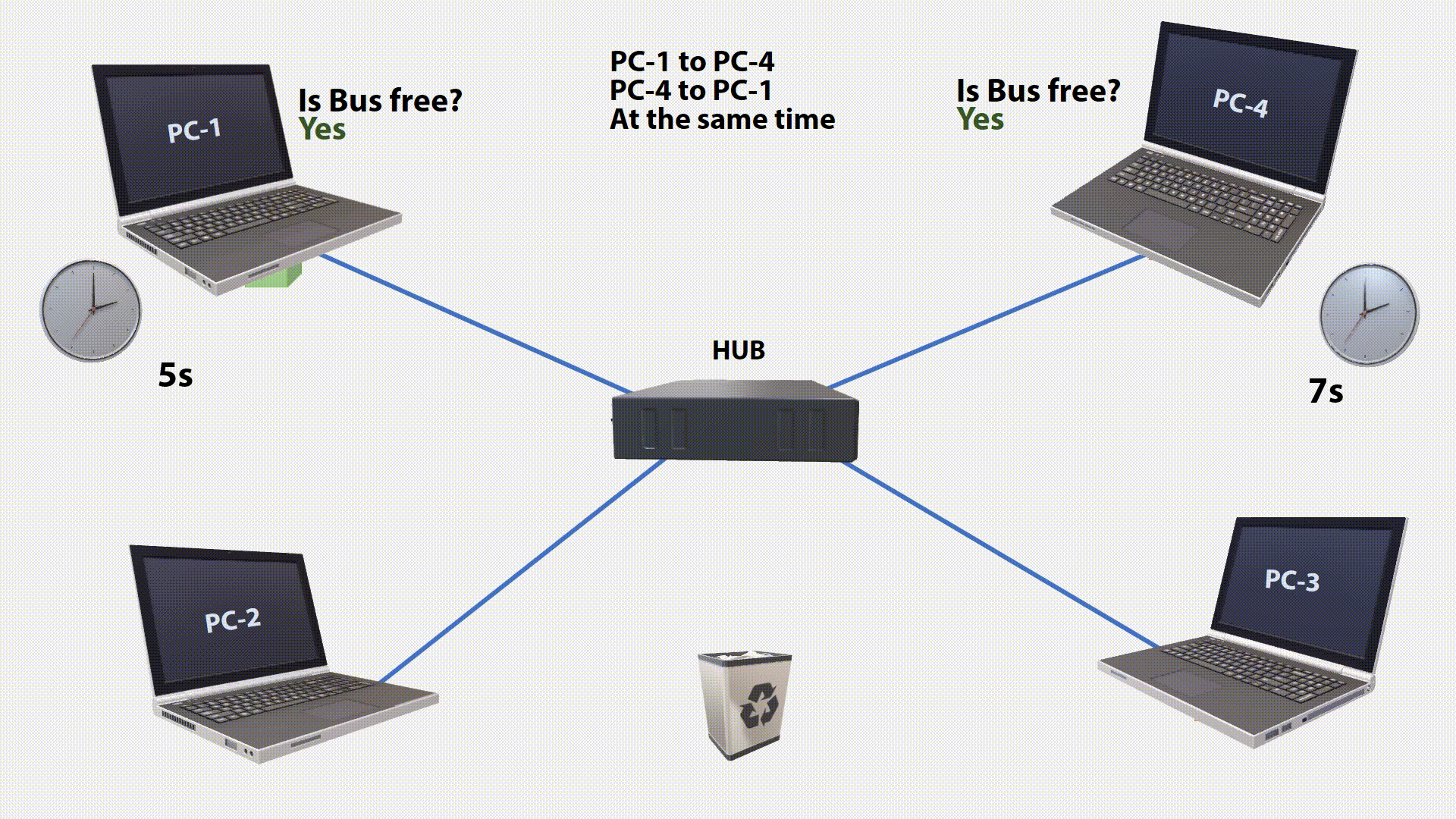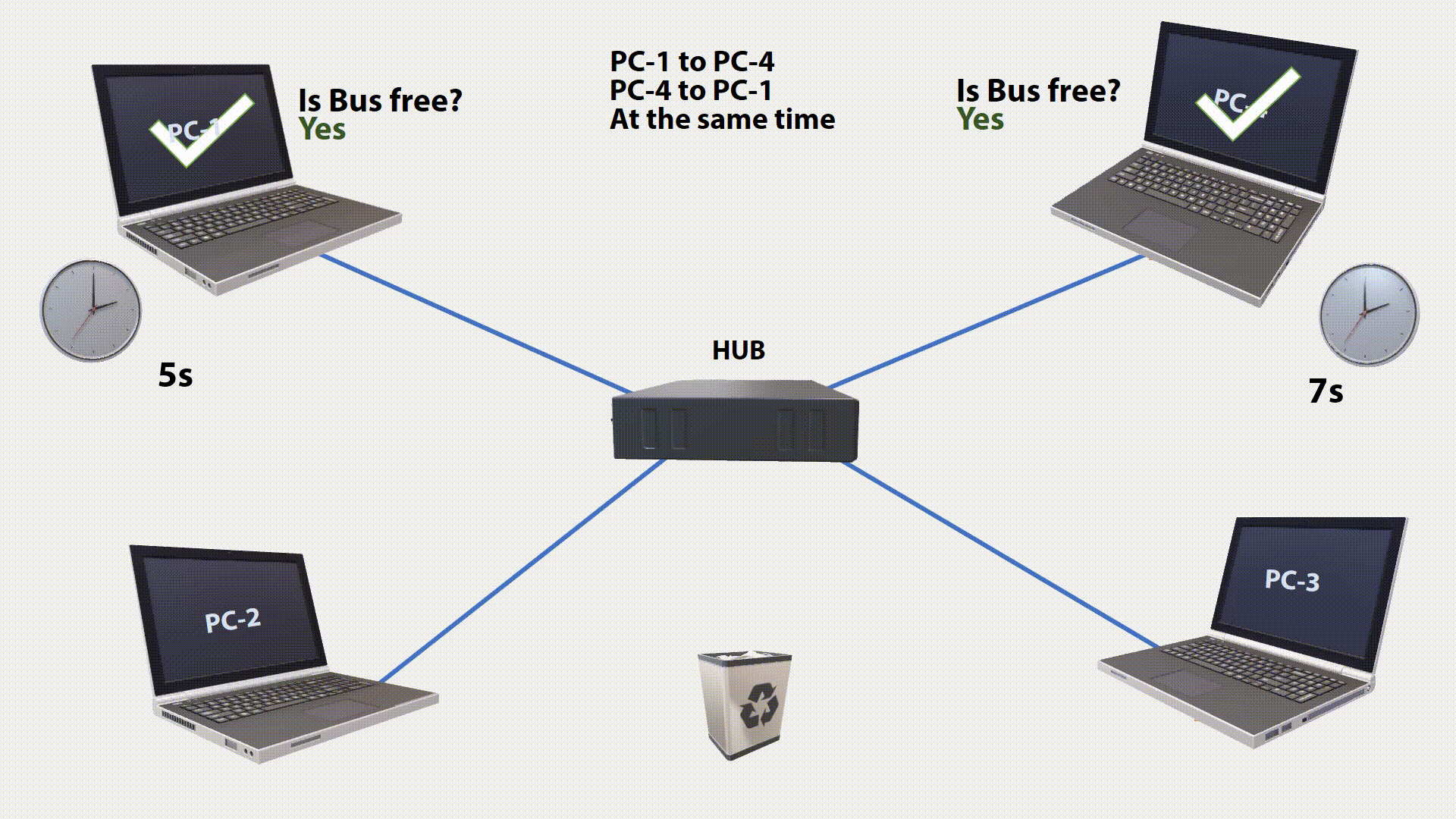
If a collision has been detected, the transfer will aborted. The transmitter that first discovers the interfering signal sends a special JAM signal so that all other stations know that the network is blocked. After a random waiting period(the last two digits(ms) of current time), it is checked again whether the bus is free. If so, it will be sent again. The process is repeated until the data is transmitted without collision(Maximum 16 Times, then its will throw away).
